SYSTEMS OF PRODUCTION
|
FORAGING
|
PASTORALISM
|
HORTICULTURE (including swidden agriculture)
|
INTENSIVE
AGRICULTURE
|
INDUSTRIALISM
|
||
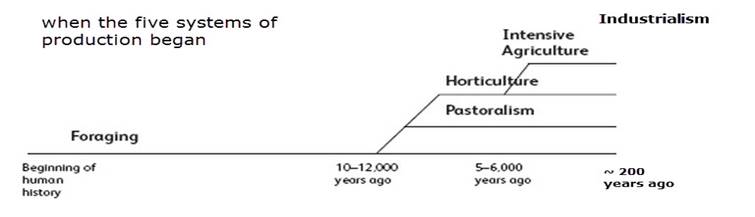
WHEN
STARTED? (NOTE THAT THESE SYSTEMS CAN GO ON AT THE SAME TIME IN DIFFERENT
PLACES. IN SOME PLACES THERE WAS A TRANSITION FROM ONE TO THE NEXT WHILE IN
OTHER PLACES THERE WAS NO CHANGE)
|
|
||||||
WHAT
IS IT
PRIMARY ENERGY SOURCE FOR GROWING THINGS, DOING WORK. SOLAR ENERGY → photosynthesis → plant matter → food for animals and energy storage (can become fossil fuels)
|
Foraging is a mode of
production involving minimal technologies to acquire food and other goods
through a combination of hunting wild animals and collecting wild plants.
SOLAR
|
Pastoralism
and horticulture started around the same time in different places
Pastoralism
From
the word “pasture,” is the production of food predominantly from the
exploitation of domesticated animals. It is what might conventionally be
called “herding” or “ranching.” Thus, the primary “work” to be done was
tending and exploiting animals such as cattle, sheep, goats, llamas, horses,
pigs, and other smaller creatures, depending on the locally available
species.
SOLAR
|
Horticulture can be defined
as farming without the use of technologies like the plow, irrigation,
fertilizer, or draft animals. In horticulture the natural environment (e.g. forest) is modified but not removed and replaced with something else like a clearer plowed field. (swidden agriculture
is the most common type of horticulture)
SOLAR
|
Intensive
agriculture is high-input, high-yield farming employing such technologies as the plow,
irrigation, fertilizer, and draft animals (all the ones missing from
horticulture). The previous environment is usually changed to something different–
permanent farmlands
SOLAR
|
Industrialism
New
kind of production based on industry or machines and machine-generated
energy.
FOSSIL FUELS, SOLAR
|
||
PLACE
|
Very
large area, low population density (why needed?)
|
Relatively
large area due to need for animal food
|
Relatively
large area due to need for fallow period
|
Smaller
total area with permanent farmlands
accessible by many people -- development of towns and cities
|
New
spatial arrangement with urban areas, agricultural areas linked by
transportation/trade networks
|
||
|
FORAGING
|
PASTORALISM
|
HORTICULTURE
(including swidden agriculture)
|
INTENSIVE
AGRICULTURE
|
INDUSTRIALISM
|
||
SOCIAL ORGANIZATION (social groups, corporate groups)
|
Small
band, usually family groupings
|
Larger
groups, kinship ties
|
Larger
groups, kinship ties
|
Much
larger groups, kinship ties expand to clan level
|
Nuclear
families and larger kinship groups restricted to domestic sphere
|
||
POLITICAL
ORGANIZATION
|
Usually
BAND
|
Usually
BAND or TRIBE
|
Usually
CHIEFDOM
|
Usually
STATE
|
STATE
|
||
PREDOMINANT
TYPE OF EXCHANGE (RECIPROCAL VS MARKET)
|
Reciprocal
|
Reciprocal
primarily
|
Reciprocal
primarily
|
Both reciprocal and market
|
Both reciprocal and market
|
||